CHANGES IN TG, ANTI TG, ANTI TPO WITH SUSPICIOUS SIGNS OF THYROID CANCER ON ULTRASOUND
Nguyen The Thanh
An Sinh Hospital
DOI: 10.47122/vjde.2020.40.3
ABSTRACT
Objective: To study the rate of positive Tg, positive AntiTg, positive AntiTPO concentration on 48 patients having thyroid ultrasounds with suspicious signs of thyroid cancer. Methods: Descriptive analysis was performed on 48 patients having thyroid ultrasounds with suspicious signs of thyroid cancer and measuring Tg, AntiTg, AntiTPO at same time from 12/2017 to 12/2018 at An Sinh hospital. Results: The rates of positive Tg, positive AntiTg, positive AntiTPO on patients having thyroid ultrasounds with suspicious signs of thyroid cancer are6,3%; 8,3%; 39,6% respectively. The rates of positive Tg, positive AntiTg, positive AntiTPO on patients with benign FNA are 10,7%; 7,1%; 39,3% respectively. On patients with follicular lesion FNA are 0%; 12,5%; 37, 5%. respectively. On patients with papillary carcinomas FNA are 0%; 10%; 40% respectively. The rate of 48 patients having thyroid ultrasounds with suspicious signs of thyroid cancer is 20.8% (10/48). Conclusions: The results show that Tg, AntiTg, Anti TPO Don’t have value in the diagnosis thyroid cancer according to thisstudy. Thyroid cancer diagnostics is mainly based on FNA in patients having thyroid ultrasounds with suspicious signs of thyroid cancer because it can be found out with high rate.
Keywords: Tg, AntiTg, AntiTPO, thyroid cancer, ultrasound.
Main correspondence: Nguyen The Thanh
Submission date: 2nd May 2020
Revised date: 13th May 2020
Acceptance date: 26th June 2020
Email: [email protected]
Tel: 0913651815
1. INTRODUCTION AND RESEARCH TARGETS
1.1. Introduction:
Thyroid cancer is still based on FNA or biopsy if there is a thyroid nodule with suspicious signs on ultrasound.
According to the medical documents, Tg and Anti Tg are considered as indicators of undifferentiated thyroid cancer such as papillary and cystic carcinoma, and papillary carcinoma is the most common which accounts for 95%, in addition there are some medical documents indicating that AntiTPO also increases in thyroid cancer.
But there are few international researches on this topic, there is none in Viet Nam.
To assess the benefit of these tests in diagnosing thyroid cancer, we decided to conduct a research on this topic.
1.2. Research targets
1.2.1.General targets
The rate of positive Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO among patients with suspicious signs of thyroid cancer on ultrasound.
1.2.2. Specific targets
The rate of positive Tg, ant Tg, anti TPO among patients with suspicious signs of thyroid cancer on ultrasound.
The rate of positive Tg, ant Tg, anti TPO among patients with FNA results of goiter.
The rate of positive Tg, ant Tg, anti TPO among patients with FNA results of follicular lesions.
The rate of positive Tg, ant Tg, anti TPO among patients with FNA results of thyroid papillary carcinoma
The rate of thyroid cancer among patients with suspicious signs on ultrasound.
2. RESEARCH SUBJECTS AND METHODS
2.1. Subjects:
Patients presented to Out – Patient Department of An Sinh hospital between December 2017 and December 2018.
2.2. Methods:
Method: Descriptive
Case Inclusion Criteria:
Patient who agreed to have their thyroid examined is acceptable. Patient whose thyroid functional tests are within normal limit, and have been tested for anti TPO, anti Tg, Tg (a test is positive when the result is higher the the upper normal limit). Ultrasound showed nodule (s) with suspicious features such as: hypoechogenicity, microcalcifications, border irregularit, or being classified as TIRADS 4 or higher.
Exclusion criteria:
Patients who did not meet case inclusion criteria.
2.3. Processing Data:
By IBM SPSS Statistics 20.
3. RESULTS
From December 2017 to December 2018, we had 48 patients presenting to out-patient department of An Sinh clinic and all of them satisfied the case inclusion criteria.
3.1. Patients’ characteristics
Gender

Age (years)

3.2. Research features
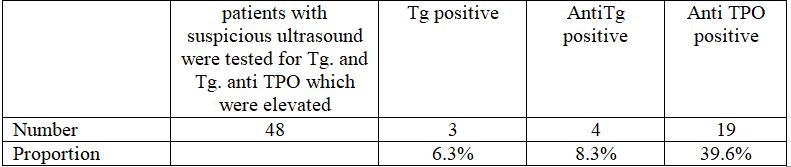
3.2.1. 48 patients with suspicious ultrasound were tested for Tg. and Tg. anti TPO
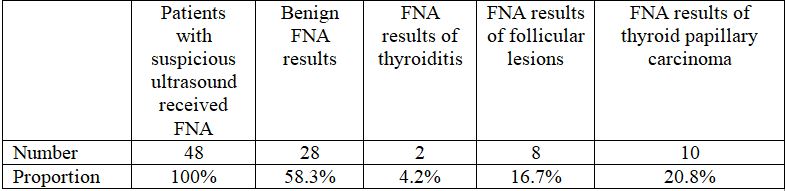
3.2.2. 48 patients with suspicious ultrasound received FNA
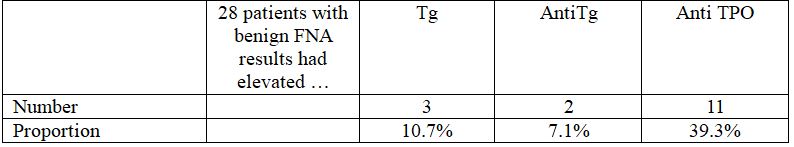
3.2.3. 28 patients with FNA results of goiter
Gender

Age (years)

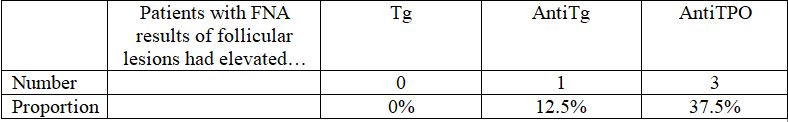
3.2.4. 8 patients with FNA results of follicular lesions
Gender

Age (years)

3.2.5. 10 patients with FNA results of thyroid papillary carcinoma
Gender

Age (years)

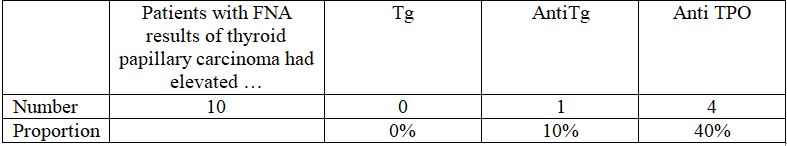
- There is no case of elevated Tg among patients with carcinoma, which is lower than among group of goiter (10.7%)
- Proportion of elevated anti Tg among group of carcinoma is higher than that among goiter patients (7.1%), in this case, may the sample size be not significantly large enough to assess..
- Proportion of elevated anti TPO in patients with carcinoma (40%) is higher that in group of goiter, but this difference is not statistically significant.
4. DISCUSSIONS
4.1. Patients’ features
4.1.1. Gender
Males take up 27.1%, Females account for 72.9%.
In most medical documents and researches on thyroid, the rate of thyroid nodule in female is higher than that in male.
4.1.2. Age
The youngest patient is 22 years old, and the oldest is 71. The average age is 46 (46,08 ±11,82). In general, there is no difference with other medical documents.
4.2. Research results
4.2.1. Positive Tg, anti Tg, anti TPO prevalance.
Among 48 patients with suspected ultrasound only 3 patients had positive Tg accounting for 6.3%, 4 patients had positive AntiTg accounting for 8.3% and 19 patients had positive AntiTPO accounting for 39.6%.
Thus, the cancer marker is not high in patients with suspected features on ultrasound, as elevated Tg takes up only 6.3% among cases.
4.2.2. Biopsy result
In 48 patients with TIRADS – 4 or higher, there were 28 patients with FNA result of goiter (benign) (58.3%), 2 patients with thyroiditis, 8 patients with follicular lesion and 10 patients with thyroid papillary carcinoma, accounting for 4.2%, 16.7%, 20.8% respectively, this means that the proportion of thyroid disease is 41.7%. This proves that FNA should be performed in patients with suspicious ultrasound as the rate of detected diseases is rather high.
4.2.3. Positive Tg, AntiTg, Anti TPO in patients with benign goiter
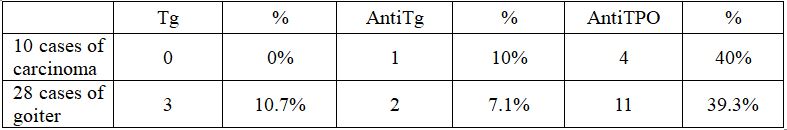
In 28 patients with benign FNA results, there were 3 patients having positive Tg (10.7%), 2 patients with elevated anti Tg (7.1%) and 11 patients with anti TPO (39.3%).
In general, positive Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO can be found among patients with benign FNA result.
4.2.4. Tg, AntiTg, Anti TPO results in patients with FNA result of follicular lesion
This kind of lesion was recorded to progress benignly in 50% cases and to advance into cancer in 50% cases.
In 8 patients with follicular lesion, there is no case of positive Tg result (0%). There is 1 case of elevated anti Tg taking up 12.5% and 3 cases of positive anti TPO (37.5%).
In comparision with group of goiter, only anti Tg was found to be higher, with 12.5% compared to 7.1%, however, it requires a larger sample size.
This shows that Tg and anti TPO test is not valuable features in diagnose this kind of lesion, and research with larger sample size is required to assess the value of anti Tg.
4.2.5. Tg, AntiTg, Anti TPO results in patients with FNA result of thyroid papillary carcinoma
In 48 patients performing FNA, there were 10 patients with thyroid papillary carcinoma, accounting for 20.83%.
In these 10 cases, there is no case of elevated Tg, while this proportion is 10.7% in group of goiter. The proportion of positive anti Tg is 10%,higher when compared to 7.1% in group of goiter, but the sample size is not large enough. Anti TPO is elevated in 40% cases, higher but not significantly than in goiter patients (39.3%). Thus, Tg and anti TPO have little value in diagnosing thyroid papillary carcinoma, and anti Tg requires researches with larger sample size to determine its value.
According to Nguyen Nghiem Luat, Tg is considered to be a biomarker of thyroid papillary carcinoma and cystic carcinoma, and Hurthle cells. It is normally tested pre-operation, pre-chemotherapy to assess the efficacy of treatment after 3 weeks, it will decrease if the treatment works, and increase again in reccurence cases. We found no case of elevated Tg in group of thyroid cancer in this research.
Vasileiadis et al. performed a research on 854 patients with total thyroidectomy: 477 cases of benign thyroid nodules and 407 cases of malignant.Patients were tested for histology and anti Tg, and this research showed that anti Tg is elevated in thyroid papillary carcinoma and concluded that anti Tg was a marker of thyroid papillary carcinoma.
Kim ES et al. performed anti TG, anti TPO tests and FNA in 1638 patients with thyroid nodules and found that the rate of elevated anti Tg among thyroid cancer patients was 30.8%, and among patients with benign goiter was 19.6%. This difference is statistically significant (p<0.001). There was no difference in Anti TPO result between patients with thyroid cancer and with goiter, leading to the conclusion that anti TPO is a independent marker for thyroid cancer.
WuX et al. performed a retrospective research on 2132 patients suffering from thyroidectomy and having anti Tg and anti TPO tested, and reported that a positive anti Tg or anti TPO was a marker for thyroid papillary carcinoma and a combination of these two indicators was more valuable.
To assume, Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO tests show little value in indicating thyroid papillary carcinoma in our research as Tg is completely absent in group of patients with thyroid papillary carcinoma while it presents in euthyroidism group. Anti Tg and anti TPO are higher among thyroid cancer patients compared to goiter group, which is in line with the findings of Vasileiadis, Kim ES and WuX, however, this difference is not noteworthy. This can be the result of a small sample size, thus further research requires a larger sample size.
5. CONCLUSIONS
- The rate of elevated Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO among patients with suspicious features for thyroid cancer is 6.3%; 8.3%; 39.6%, respectively.
- The rate of elevated Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO among patients with FNA result of goiter is: 6,3%; 8,3%; 39,6%, respectively.
- The rate of elevated Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO among patients with FNA result of follicular lesion is: 0%;12,5%; 37,5%, respectively.
- The rate of elevated Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO among patients with FNA result of thyroid papillary carcinoma is 0%;10%;40%, respectively.
- The rate of thyroid papillary carcinoma among 48 patients with suspicious ultrsound features is 20.8% (10/48).
As these Tg, anti Tg and anti TPO has not shown value in indicating thyroid cancer, diagnosis is mainly confirmed by FNA in group of patients with suspiscious signs on ultrasound, where thyroid cancer has been detected frequently
REFERENCES
- Nguyễn Nghiêm Luật. Thyroglobulin (Tg): Biomarker of thyroid papillary carcinoma and cystic carcinoma, https://medlatec.vn/chi-tiet/can-lam-sang/thyroglobulin-tg-dau-an-cua-ung-thu-tuyen-giap-the-nhu-va-the-nang–22-6434.aspx
- Nguyễn Thế Thành. Thyroid carcinoma and alarming signs. Journal of Endocrine and Diabetes, Vietnamese Association of Diabetes and Endocrine. Volume 16, 2016. page 53-56.
- Nguyễn Thế Thành. Prevalence of euthyroid goiter among female patients presenting to general check-up at An Sinh hospoital. Yearbook of science of An Sinh hospital 2016.page 37-42.
- Nguyễn Thị Xuyên, Lương Ngọc Khuê , Thái Hồng Quang. “Guideline on diagnosis and treatment of metabolic and endocrinology disease”. Simple Goiter (p 101-104). Ha Noi Medical Publishing House 2015.
- Nguyễn Thị Xuyên, Lương Ngọc Khuê , Thái Hồng Quang. “Guideline on diagnosis and treatment of metabolic and endocrine disease”. Thyroid carcinoma (p 127-141). Ha Noi Medical Publishing House – 2015.
- Kim ES1, Lim DJ, Baek KH, Lee JM, Kim MK, Kwon HS, Song KH, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY. Thyroglobulin antibody is associated with increased cancer risk in thyroid nodules. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20465529. 2010 Aug;20(8):885-91.
- C, Ph.D., F.A.C.B President, 2001-2002, American Thyroid Association. Thyroglobulin (Tg) and Tg Antibody (TgAb) Testing for Patients Treated for Thyroid Cancers. http://www.thyca.org/pap-fol/more/thyroglobulin/
- Todd B. Nippoldt, M.D. What is a thyroid peroxidase antibody test? Does it diagnose thyroid disease? http://www.mayoclinic.org/thyroid-disease/expert-answers/faq-20058114
- Vasileiadis I1, Boutzios G, Charitoudis G, Koukoulioti E, Karatzas T. Thyroglobulin antibodies could be a potential predictive marker for papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol.2014 Aug;21(8):2725-32. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24595799
- Wu X1, Lun Y, Jiang H, Gang Q, Xin S, Duan Z, Zhang J. Coexistence of thyroglobulin antibodies and thyroid peroxidase antibodies correlates with elevated thyroid-stimulating hormone level and advanced tumor stage of papillary thyroid cancer. 2010 Aug; 20(8):885-91. doi: 10.1089/thy.2009.0384. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20465529
 Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam
Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam