EVALUATING THE INFLUENCE OF DIABETIC COMPLICATIONS
ON THE QUALITY OF LIFE BY THE QUESTIONAIRE SHORT FORM-36
IN THE TYPE 2 DIABETIC PATIENTS
Dua Dao Thi, Duy Thanh Nguyen,
Trong Nghia Nguyen, Thua Nguyen Tran
Hue Central Hospital
ABSTRACT
Background: Diabetes is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and causes many complications that significantly affect the quality of life of patients. Objectives: 1/To evaluate the quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients through the questionaire Short Form-36; 2/To survey the influence of some complications on the quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients. Subjects and Methods: 328 patients were diagnosed with diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association, 2015. Research by the method described cross, convenient sampling. Results: Quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients was 50.58 ± 20.59 points, physical health in type 2 diabetic patients was 51.62 ± 21.81 points, and mental health was 49.90 ± 18.58 points. Complications were influence significantly on both Physical health and mental health of type 2 diabetic patients. Conclusion: Quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients was 50.58 ± 20.59 points. Complications were independent influence significantly on the quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients.
Main correspondence: Dao Thi Dua
Submission date: 1st August 2018
Revised date: 18th August 2018
Acceptance date: 31th August 2018
- BACKGROUND
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a endocrine and metabolic which is characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and causes many complications that significantly affect the quality of life of patients. Quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients is a problem being interested. Therefore, we conduct this title to aim two these objectives:
1/ To evaluate the quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients through the questionnaire Short Form 36 (SF-36).
2/ To survey the influence of some complications on the quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients.
2. SUBJECTS AND METHODS
2.1. Subjects: Type 2 diabetic patients treated at Hue Central Hospital, diagnosed diabetes according to the American Diabetes Association, 2015 and diagnosed with type 2diabetes according to some classified standards WHO 2005.
2.2. Methods:
2.2.1. Designs:
Research by the method described cross, convenient sampling.
including328 patients were diagnosed with type 2 diabetic patients satisfying the standards.
2.2.2. Variables:
– Evaluate some complications in type 2 diabetic patients.
+ Macrovascular complications:
* Coronary artery disease (CAD): diagnose according to history of disease, clinical, ECG, echocardiography.
* Peripheral vascular disease (Complications Artery of lower extremities): clinical, Doppler ultrasound of lower extremities artery show that atherosclerosis causing narrow or embolism.
* Cerebrovasculardisease (CVD): history of stroke, brain CT scanner, Doppler ultrasound of carotid artery.
+ Microvascular complications:
* Diabetic retinopathy: diagnoseaccording to opthalmoscopy oroptical tomography show diabetic retinopathy.
* Diabetic nephropathy: diagnose according to proteinuria, decreased glomerular filtration function estimated according to Cockcroft Gault formula.
+ Hypoglycemia, thehistory of emergency hyperglycemia.
+ Infection: infectious focus.
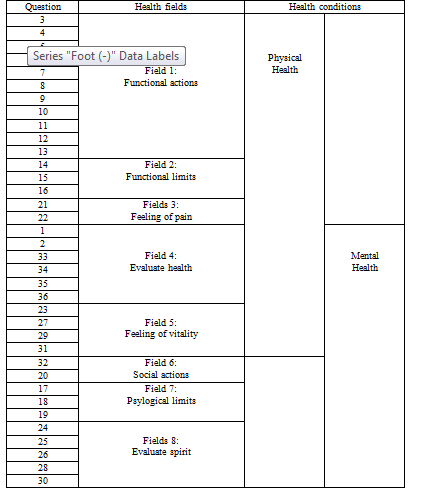
– Quality of life: Total score of quality of life is average of 8 health fields.
Table 2.2. Health fields and conditions
 – Record scores of questionaire SF-36: The answers are scored from 0 to 100, score 100 is the best representation for quality of life of patients (Table 2.3)
– Record scores of questionaire SF-36: The answers are scored from 0 to 100, score 100 is the best representation for quality of life of patients (Table 2.3)
Table 2.3. Score of answers
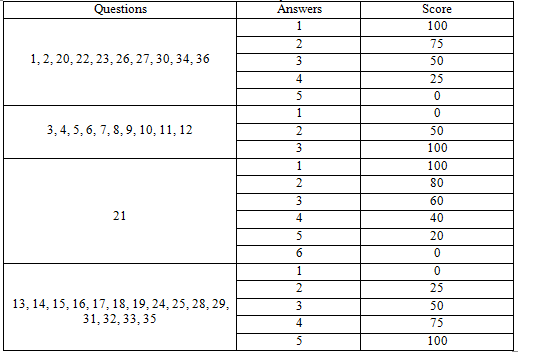 2.2.3. Processing and analyzing data: Information from questionaire SF-36 will be encoded and entering in Excel – Classification of Quality of Life according to SF 36:Weak: 0-25 points. Medium: >25-50 points. Above average: >50- 75 points. Good: >75 points and processed by SPSS softwave.
2.2.3. Processing and analyzing data: Information from questionaire SF-36 will be encoded and entering in Excel – Classification of Quality of Life according to SF 36:Weak: 0-25 points. Medium: >25-50 points. Above average: >50- 75 points. Good: >75 points and processed by SPSS softwave.
3. RESULTS
Table 3.1. General characteristics of type 2 diabetic patients
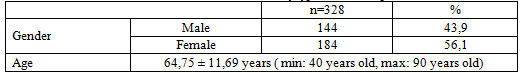
Female patients make up 56,1%; Average age is 64,75 ± 11,69 years.
Table 3.2. Some complications of type 2 diabetic patients
| Complications n % | Complications n % |
| CAV 15 4,6
P vascular disease 30 9,1 CVD 38 11,6 |
Diabetic Retinopathy 62 18,9
Diabetic Nephropathy 72 22 Infection 138 42,1 Hypoglycemia 26 7,9 |
Microangiopathies were more common
Table 3.3. Health fields and classification of quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients
| 8 health fields | n | Average |
| Functional actions | 328 | 74,09 ± 27,89 |
| Functional limits | 328 | 34,22 ± 37,21 |
| Feeling of pain | 328 | 48,46 ± 22,29 |
| Evaluating health | 328 | 43,72 ± 21,32 |
| Feeling of vitality | 328 | 58,72 ± 15,39 |
| Social actions | 328 | 51,98 ± 17,33 |
| Psychological limits | 328 | 37,41 ± 38,82 |
| General spirit | 328 | 56,71 ± 14,56 |
| Physical health | 328 | 51,62 ± 21,81 |
| Mental health | 328 | 49,90 ± 18,58 |
| Quality of life | 328 | 50,58 ± 20,59 |
| Weak | 45 | 13,7 |
| Medium | 118 | 36 |
| Above average | 112 | 34,1 |
| Good | 53 | 16,2 |
Quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients: 50,58 ± 20,59 points.
Physical health:51,62 ± 21,81points.
Mental health:49,90 ± 18,58points.
Table 3.4. Influence of complications on Quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients
| Complications | FA | FL | FoP | EH | FoV | SA | PL | GS | Δ |
| CAV
Yes No |
47 75,38 |
8,33 35,46 |
28,73 49,41 |
25,33 44,60 |
42,67 59,49 |
39,20 52,60 |
11,07 39,73 |
40,80 57,47 |
13,4 →28,66 |
| P.VascularYes
No |
52,00 76,31 |
8,33 36,83 |
25,90 50,73 |
23,90 45,72 |
42,83 60,32 |
34,33 53,76 |
12,13 41,06 |
42,67 58,12 |
15,45 →28,93 |
| CVD
Yes No |
38,03 78,81 |
8,55 37,59 |
29,61 50,93 |
22,47 46,51 |
40,92 61,05 |
34,00 54,34 |
6,11 42,65 |
41,68 58,68 |
17 →40,78 |
| D.Nephropathy
Yes No |
60,83 77,81 |
18,06 38,77 |
38,46 51,27 |
31,69 47,11 |
50,28 61,09 |
44,64 54,05 |
20,76 43,38 |
47,25 59,37 |
9,41 →22,62 |
| D. Retinopathy
Yes No |
60,16 77,33 |
12,10 39,38 |
36,82 51,17 |
31,87 46,48 |
50,56 60,62 |
44,90 53,64 |
20,90 42,50 |
49,16 58,47 |
8,74 →27,28 |
| Infection
Yes No |
72,54 75,21 |
31,52 36,18 |
46,36 49,99 |
39,99 46,43 |
55,94 60,74 |
49,28 53,95 |
35,19 40,76 |
54,36 58,41 |
2,67 → 6,44 |
| Hypoglycemia
Yes No |
70,00 74,44 |
14,42 35,93 |
38,69 49,30 |
36,69 44,33 |
57,31 58,84 |
50,04 52,15 |
25,50 39,53 |
55,85 56,78 |
0,93 →21,51 |
FA: Functional actions, FL: Functional limits, FoP: Feeling of pain, EH:Evaluate health, FoV: Feeling of Vitality, SA: Social actions, PL: Psychological limits, GS: General Spirit, Δ: fluctuation of score of 8 health fields between group with complications and group without complication
Chart 3.8. Influence of CAD on Quality of life
The quality of life in patients with complications descrease in coparison with patients without complications.
Table 3.5. Influence of complications on Physical Health
| Complication | FA
n= 328 |
FL
N= 328 |
FoP
n= 328 |
EH
n= 328 |
PH
n= 328 |
| CAV
Yes No |
47,00±25,76
75,38±27,36 p<0,01 |
8,33±15,43
35,46±37,50 p<0,01 |
28,73±15,52
49,41±22,14 p<0,01 |
25,33±17,36
44,60±21,11 p<0,01 |
30,27±14,36
52,65±21,59 p<0,01 |
| P.Vascular
Yes No |
52,00±32,47
76,31±26,44 p<0,01 |
8,33±21,10
36,83±37,50 p<0,01 |
25,90±15,92
50,73±21,58 p<0,01 |
23,90±15,97
45,72±20,77 p<0,01 |
30,20±16,28
53,78±21,14 p<0,01 |
| CVD
Yes No |
38,03±24,64
78,81±24,67 p<0,01 |
8,55±21,96
37,59±37,50 p<0,01 |
29,61±15,82
50,93±21,84 p<0,01 |
22,47±12,56
46,51±20,66 p<0,01 |
27,53±14,50
54,78±20,61 p<0,01 |
| D. Nephropathy
Yes No |
60,83±29,88
77,81±26,18 p<0,01 |
18,06±29,43
38,77±37,94 p<0,01 |
38,46±18,01
51,27±22,59 p<0,01 |
31,69±16,72
47,11±21,27 p<0,01 |
39,62±18,91
55,00±21,41 p<0,01 |
| D. Retinopathy
Yes No |
60,16±31,02
77,33±26,12 p<0,01 |
12,10±21,58
39,38±38,21 p<0,01 |
36,82±18,21
51,17±22,31 p<0,01 |
31,87±17,98
46,48±21,11 p<0,01 |
38,08±17,76
54,78±21,48 p<0,01 |
| Infection
Yes No |
72,54±29,45
75,21±26,72 p>0,05 |
31,52±30,03
36,18±38,01 p>0,05 |
46,36±23,27
49,99±21,48 p>0,05 |
39,99±20,33
46,43±21,66 p<0,01 |
49,03±21,95
53,01±21,57 p>0,05 |
| Hypoglycemia
Yes No |
70,00±24,08
74,44±28,20 p>0,05 |
14,42±23,63
35,93±37,69 p<0,01 |
38,69±18,52
49,30±22,41 p<0,05 |
36,69±15,11
44,33±21,68 p<0,05 |
43,12±15,13
52,35±22,15 p<0,01 |
Chart 3.9. Influence of peripheral vascular disease on quality of life.
Type 2 diabetic patients with peripheral vascular disease will be influenced on 8 health fields in comparison with patients without this complication.
Table 3.6. Influence of complications on Mental health
| Complications | FoV
n= 328 |
SA
n= 328 |
PL
n= 328 |
GS
n= 328 |
PH
N= 328 |
| CAV
Yes No |
42,67±13,34
59,49±15,07 p<0,01 |
39,20±14,12
52,60±17,24 p<0,01 |
11,07±20,56
39,73±39,01 p<0,01 |
40,80±10,38
57,47±14,31 p<0,01 |
31,80±13,23
50,77±18,37 p<0,01 |
| P.Vascular Yes No | 42,83±14,00
60,32±14,61 p<0,01 |
34,33±10,94
53,76±26,85 p<0,01 |
12,13±22,20
41,06±39,16 p<0,01 |
42,67±11,79
58,12±14,06 p<0,01 |
30,83±12,63
51,82±18,00 p<0,01 |
| CVD
Yes No |
40,92±23,34
61,05±14,19 p<0,01 |
34,00±14,06
54,34±16,31 p<0,01 |
6,11±18,70
42,65±38,79 p<0,01 |
41,68±13,30
58,68±13,55 p<0,01 |
28,92±12,18
52,65±17,49 p<0,01 |
| D.Nephropathy Yes No | 50,28±15,19
61,09±14,61 p<0,01 |
44,64±15,04
54,05±17,38 p<0,01 |
20,76±31,85
43,38±39,20 p<0,01 |
47,25±13,85
59,37±13,64 p<0,01 |
38,76±15,54
53,03±18,18 p<0,01 |
| D.Retinopathy Yes No | 50,56±14,63
60,62±14,96 p<0,01 |
44,90±15,47
53,64±17,34 p<0,01 |
20,90±30,91
42,50±39,38 p<0,01 |
49,16±14,76
58,47±13,96 p<0,01 |
39,37±15,94
52,35±18,31 p<0,01 |
| Infection
Yes No |
55,94±16,63
60,74±14,93 p<0,01 |
49,28±18,13
53,95±16,48 p<0,05 |
35,19±38,18
40,76±39,20 p>0,05 |
54,36±14,85
58,41±14,14 p<0,05 |
46,84±18,25
52,12±18,54 p<0,05 |
| Hypoglycemia Yes No | 57,31±13,05
58,84±15,58 p>0,05 |
50,04±15,77
52,15±17,46 p>0,05 |
25,50±28,74
39,53±39,40 p<0,05 |
55,85±14,77
56,78±14,56 p>0,05 |
44,92±14,32
50,33±18,86 p>0,05 |
The chronic complications descreasing scores of quality of life
Chart 3.10. Influence of CVD on Quality of life
Type 2 diabetic patients with CVD will be influenced on 8 health fields in comparison with type 2 diabetic patients without this complication.
Chart 3.11. Influence of diabetic nephropathy on Quality of life
Type 2 diabetic patients with diabetic nephropathy will be influenced on 8 health fields in comparison with type 2 diabetic patients without this complication.
Table 3.7. Influence of complications on Quality of life type 2 diabetic patients
multiple-variable recurrent analysis
| Complications | Physical health | Mental health | ||||||
| β | β adjustment | T | p | β | β adjustment | t | p | |
| Constance | -141,95 | -8,670 | <0,01 | -117,82 | -8,589 | <0,01 | ||
| CAV | 7,854 | -0,142 | 3,287 | <0,01 | 6,909 | 0,147 | 3,451 | <0,01 |
| P.Vascular | 17,895 | 0,237 | 5,413 | <0,01 | 15,809 | 0,246 | 5,708 | <0,01 |
| CVD | 29,254 | 0,43 | 9,983 | <0,01 | 25,398 | 0,438 | 10,34 | <0,01 |
| D.Nephropathy | 9,824 | 0,187 | 3,671 | <0,01 | 10,449 | 0,233 | 4,661 | <0,01 |
| D. Retinopathy | 11,462 | 0,206 | 4,053 | <0,01 | 7,579 | 0,160 | 3,199 | <0,01 |
| Infection | 5,721 | 0,13 | 2,919 | <0,01 | 6,015 | 0,160 | 3,663 | <0,01 |
| Hypoglycemia | 11,492 | 0,143 | 3,285 | <0,01 | 8,010 | 0,117 | 2,716 | <0,01 |
| Hyperglycemia | 2,154 | 0,028 | 0,631 | >0,05 | 2,804 | 0,042 | 0,981 | >0,05 |
Multiple-variable recurrent equation:
* Physical health = -141,95 + 7,854 (CAV) + 17,895 (P.Vascular) + 29,254 (CVD) + 9,824 (D. Nephropathy) + 11,462 (D. Retinopathy) + 5,721 (Infection) + 11,492 (Hypoglycemia) + 2,154 (Emergency Hyperglycemia).
* Mental health = -117,816 + 6,909 (CAV) + 15,809 (P.Vascular) + 25,398 (CVD) + 10,449 (D. Nephropathy) + 7,579 (D. Retinopathy) + 6,015 (Infection) + 8,01 (Hypoglycemia) + 2,804 (Emergency Hyperglycemia).
- DISCUSSION
4.1. The quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients through the questionnaire Short Form-36: This research shows the quality of life of type 2 DM patients was 50,58 ± 20,59 points, belonging to above average level. In that, physical health:51,62 ± 21,81points, mental health:49,90 ± 18,58points, field of functional actions was highest and the field of functional limits was lowest.
Compare with other researches in Vietnam and abroad.
|
Quality of life |
S.Sawsan 2015 | B.Natasha
2014 |
Khoa Vo Tuan | Our research 2015 | |
| No DM | DM | ||||
| Functional actions | 61,2 | 85 | 95,6 | 63,3 | 74,09 |
| Functional limits | 19,6 | 65 | 86,1 | 45,8 | 34,22 |
| Feeling of pain | 59,3 | 78 | 80 | 49,3 | 48,46 |
| Evaluating health | 56,5 | 58 | 59,1 | 34,7 | 43,72 |
| Feeling of vitality | 53 | 57 | 73 | 43,3 | 58,72 |
| Social actions | 55,4 | 90 | 88,5 | 52,4 | 51,98 |
| Psychological limits | 57,4 | 69 | 75 | 55,6 | 37,41 |
| General spirit | 55,6 | 78 | 64,9 | 50,8 | 56,71 |
| Physical health | 41,1 | 45 | 78,76 | 47,28 | 51,62 |
| Mental health | 42,1 | 52 | 72,1 | 47,36 | 49,90 |
The research of Khoa Vo Tuan showed that quality of life of diabetic group fluctuate from
34,7 to 63,3 points; In which, In that field of functional actions was highest and the field of evaluating health was lowest[17]. Many researches recorded that DM was one of causes having influence considerately on mental health in patients such asdepression, anxiety…. Hillary Bogner also realized thatDM patients easily suffered depression, 50% of DM patients suffering depression died after 2 years if depression wasn’t treated [4]. Firooze D researched on 330 DM patients, there is 58,2% having symptoms of depression and quality of life of DM patients suffering depression descreased strongly in comparison with DM patients without, Quality of life of DM patients with and without depression is 50,7 and 60,5 points[2]. Like this, in comparison with people without DM, Quality of life of DM patents descreases strongly. Our research’s result is also suitable with comments of some authors. Quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients: 50,58 ± 20,59 points.
Physical health: 51,62 ± 21,81points.
Mental health: 49,90 ± 18,58points.
4.2. The influence of some complications on the quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients: This research’s result shows that chronic complications such as coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic retinopathy influence on 8 health fields in DM patients, scores of quality of life descreasing strongly compared with group without complications with p<0,001. After rejecting the interfering factors, those complications also influence on quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients considerately.
Coronary artery disease:
Research’s result oftype 2 diabetic patients with CAD showed that quality of life descrease in 8 fields compared with patients without CAD, descrease scores of 8 health fields from 13,4 to 28,66 points. The research of Kontodimopoulos N. And Coworker showed that after adjusting the interfering factors, the quality of life of patients suffering CAD descrease significantly in comparison with patients without CAD[10]. An adding analysis in Sweden with 19 researches show that CAD is one of factors influence most on quality in DM patients[15]. Our research also show the similar result.
Complications Artery of lower extremities: Type 2 diabetic patients with complications ofartery of lower extremities, the quality of life descrease in 8 fields compared with patients without this complication, descrease scores of 8 health fields from 15,45 to 28,93 points. Khoa Vo Tuan research about quality of life of patients after extremities amputation getting less score than group without extremities amputation [17]. A research in Sweden with 457 objectatives in order to evaluate influence of diabetic foot on quality of life of DM also show the similar result[1].
Cerebrovasculardisease:
Type 2 diabetic patients with cerebrovascular disease will be influenced on 8 health fields in comparison with DM patients without this complication, descrease scores of 8 health fields from 17 to 40,78 points. A lot of researches show that stroke isone of complications influence most on quality of life in DM patients. In reasearches about relationships between complications and quality of life in DM patients carried out on 1000 subjects in Nauy, result is stroke influence on almost health fields of patients[14].
Diabetic retinopathy and Diabetic nephropathy:
This research shows the quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients have diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy decrease in comparison with group without these complications with p<0,05. Characteristics of diabetic nephropathyis proteinuria and the end stage is kidney failure. When there is proteinuria, patients start appear edema, hypertension, glycemic control difficultly, or hypoglycemia and influence on both physical and mental health[13]. In the third stage of diabetic nephropathy the symptoms are often reserve until progressing to macro albuminuria and kidney failure then influence strongly on quality of life [3]. Diabetic retinopathy influence on patients’s mental healthdue to symtoms such as Glaucoma, cataract, sudden blind [3]. Wulsin L.R.’s research shows the similar result.
Infections in DM patients.
This research noted the infection only influence on some fields of quality of life, mainly in mental health. Because infection only need intensive treatment to recocer completely, but it easily recur and the time of treatment is longer, it show also influence on hypoglycemia and easily leads to hyperglycemia such as Keto Acidosis.
Hypoglycemia:
Depend on level of hypoglycemia to influence on quality of life, In this research most of patients are old, many patients could not realize the symptoms of hypoglycemia and treat hypoglycemia condition by themselves at home. Many case of coma hospitalizing, there are some case show stroke or heart infarction, influence on physical health and mental health of patients [13].
In a cross-sectional research about relationship between the symptoms of hypoglycemia and patients’s quality of life conducted in 7 Europe countries, Fernando A.G and coworker researched in 1709 patients and 38% of them recorded that they used to have the symptoms of hypoglycemia within 12 months from the day they started to research. In which, 68% of patients recorded that they only had slight symptoms, 27% medium symptoms, 5% severe symptoms [5]. According to results, the symptoms of hypoglycemia influence on patients’s quality of life and the more severe symptoms are, the more patients’s quality of life are influenced.
CONCLUSIONS
– Quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients was 50,58 ± 20,59 points, belonging to above average level. Physical health of type 2 diabetic patients was 51,62 ± 21,81 points, belonging to above average typeand mental health is 49,90 ± 18,58 points, belonging to medium type.
– Vascular complications influence on all 8 health fields of diabetic patients, Quality of life of type 2 diabetic patients with vascular complications descrease considerately in compare with non-complications with p<0,001.
REFERENCES
- Berardis de G., Pellegrini F. and Franciosi M. (2005), “Longitudinal assessment of quality of life in patients with type 2 diabetes and self reported erectile dysfunction“, Diabetes Care. 28, pp. 2637-2643.
- Bergmann N. (2014), “Diabetes and ischemic heart disease: double jeopardy with regard to depressive mood and reduced quality of life“, Endocrine connections, pp. 156-160.
- Bozidar V. and Tamara T. (2012), “Diabetic nephropathy“, Pathophysiology and complications of diabetes mellitus, pp. 71-89.
- Faith Dickerson and Clayton H. (2006), “Quality of life in individuals with serious mental illness and type 2 diabetes“, diabetes Care, pp. 31-39.
- Fernando G., Donald D. Y. and Gonzalo N. (2010), “Association of hypoglycemic symptoms with patients’ rating of their health-related quality of life state: a cross sectional study“, Health and quality of life outcomes, pp. 1-8.
- Glasgow R. E., Ruggiero L. and Eakin E. G. (1997), “Quality of life and associated characteristics in a large national sample of adults with diabetes“, Diabetes Care. 20, pp. 562-567.
- Hakan Demirci. and Cinar Y. (2012), “Quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients in primary health care“, Danish Medical Journal.
- Kazemi-Galougahi M. H. and Ghaziani H. N. (2012), “Quality of life in type 2 diabetic patients and related effective factors“, Indian Journal of medical sciences. 66, pp. 230-237.
- Knezevic A. and Tatjana S. (2015), “Assessment of quality of life in patients after lower limb amputation“, Med Pregk, pp. 103-108.
- Koukoulis G., Melidonis A. and Milios K. (2015), “Quality of life of insulin-native people with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on oral antidiabetic drugs after the addition of insulin Glargine, in every day clinical practice in Greece“, Journal of diabetes, metabolic disorders & control 2(2), pp. 1-9.
- Lau C.Y. and Qureshi A.K. (2004), “Association between glycaemic control and quality of life in diabetes melitus“, J Postgrad Med. 50, pp. 189-194. Shanableh S. and Abdulkarem A. (2015), “Quality of life of diabetic patients on different types of antidiabetic medications“, International journal of pharmaceutical sciences and research. 6(8), pp. 3467-3471.
- Mai Văn Hoàng và Nguyễn Hữu Kỳ (2008), Đặc điểm lâm sàng và các yếu tố liên quan đến rối loạn trầm cảm ở bệnh nhân đái tháo đường tại khoa nội tiết Bệnh viện Trung ương Huế, Luận văn tốt nghiệp Bác sĩ Y khoa, Đại học Y Dược Huế.
- Manjunatha K. and Sarsina O. D. (2012), “Bio-chemical aspects, pathophysiology of micro albuminuria and glycated hemoglobin in type 2 diabetes mellitus“, Pathophysiology and complications of diabetes mellitus, pp. 19-44.
- Quah J. H. M., Luo N. and Ng W. Y. (2011), “Health-related quality of life is associated with diabetic complications, but not with short-term diabetic control in primary care“, Annals Academy of Medicine Singapore, pp. 276-286.
- Ramzy S., MerhanSamy S. and Badary O. (2015), “Improvement in clinical outcomes of type 2 diabetic patients after pharmacist- physician colllaborative care for dyslipidemia“, International journal of advanced research. 3(3), pp. 211-215.
- Sorensen E. R. and Bjorner J. B. (2007), “Diabetic patients treated with dialysis: complications and quality of life“, Diabetologia, pp. 2254-2262.
- Võ Tuấn Khoa (2007), Nghiên cứu về bảng đánh giá chất lượng cuộc sống short form 36 và ứng dụng để đánh giá chất lượng cuộc sống cho bệnh nhân đái tháo đường sau đoạn chi tại Bệnh viện Chợ Rẫy, Luận văn Thạc sĩ Y học, Đại học Y dược Hồ Chí Minh.
 Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam
Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam