Hypertension and some risk factors in patients with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Tran Nam Quan
Endocrine Center in Khanh Hoa Province
ABSTRACT
Objective: To evaluate the characteristics of hypertension and to define the relationship between the hypertension with some risk factors (age, gender, family history of diabetes, BMI, waist circumference, dyslipidemia) in patients with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes.Methods: Adescriptive cross-sectional study was conducted on 252 subjects with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes from July 2015 to October 2016 in Khanh Hoa.Results: The prevalence of hypertension was 55.2% in which level 2 hypertension accounted for the highest proportion. 71.2% diabetic subjects ≥ 45 years of age is hypertensive comapred to only 28.2% in patients < 45 years of age. Hypertension was more frequent in patients with increasing age, with high level of hypertension and with family history of diabetes (64.7% in subjects with a family history vs only 35.3% in patients without family history p <0.05). The proportion of hypertension was more significantly frequent in subjects with BMI ≥ 23 than in patients with normal BMI (77.7% vs 22.3%, respectively); with increasing waist circumference (86.3% vs 13.7%); with microalbuminuria (+) (71.9% vs 28.1%); with dyslipidemia (88.5% vs 11.5%).Conclusions: The prevalence of hypertension in patients with newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus was 55.2%, there was a statistically significant relationship between hypertension and family history of diabetes, BMI ≥ 23 (overweight, obesity), abdominal obesity and dyslipidemia.
Keywords: hypertension, risk factors, newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
Main correspondence:Tran Nam Quan
Submission date: 8 Feb 2017
Revised date: 20 Feb 2017
Acceptance date: 15Mar 2017
I. QUESTION
Hypertension in patients with diabetes are very common and are factors that increase the severity of diabetes. The rate of hypertension in these patients is higher than in people without diabetes.
In Vietnam there are many studies on the situation of hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes, but in patients with diabetes have been diagnosed and treated later stage. No studies on hypertension in many stages of type 2 diabetes discovered for the first time.
Therefore, we conducted a study entitled “Survey on hypertension and some risk factors involved in patients with type 2 diabetes discovered for the first time” with two objectives were: One is review the characteristics of hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes nhandai first detected. Two is determine the association between hypertension and some risk factors such as age, gender, family history related to diabetes, BMI, waist circumference risk, hypertension and disorders hyperlipidemia in patients with type 2 diabetes discovered for the first time.
II. SUBJECTS AND METHODS
1.1. Research subjects: We studied two hundred and fifty-two subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus is first detected at the Center for Endocrinology Khanh Hoa according to the following criteria:
1.1.1. Patient selection criteria:
1.1.1.1. Criteria for diagnosis of diabetes : In the study we used standard fasting venous plasma glucose ≥ 7 mmol / l and was tested twice at two different times to diagnose diabetes.
1.1.1.2. Diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes: Apply some standard WHO classification 2002:
In the study we used the standards generally older age at onset, diagnosed obesity in type 2 diabetes.
1.1.2. Exclusion criteria:
Not included in the team for the patient physiological condition or disease affecting the excretion of microalbuminuria as: Macroscopic hematuria or proteinuria broadly ; Liver failure, kidney failure, nephritis, urinary tract infections ; Fever ; Physical activity sharply in yesterday.; Infection ; Congestive heart failure. ; Severe dehydration, pregnancy.; Those who do not agree to participate in research.; These patients have been detected and treated earlier diabetes.; Patients with hypertension are treated with ACE inhibitors
1.1.3. Time and place of study: Research period: from July 2015 to October 2016. Research area: Centre for Endocrinology, Khanh Hoa province.
1.2. Research methods:
1.2.1. Research design:
Using the method described cross-sectional studies have analyzed. Convenience sample is taken continuously during the study. The sample size was calculated using the formula: ![]()
. Inside: 95% reliability, then Z2α / 2 = 1.96; p: Prevalence of hypertension in people with type 2 diabetes discovered estimate is 0.2. ; q = 1 – p = 0.8; d: is the absolute accuracy of 0.05 obtained;
n = 245. We surveyed 252 people.
1.2.2. Data collection: After examining records of administrative information, the patient has no exclusion criteria will be taking blood glucose test. The blood glucose of patients with ≥ 7 mmol / l was conducted testing of total urine analysis to exclude cases of proteinuria, hematuria or urinary positive leukocytes in urine.. Recognition of the administrative information and clinical family history related to diabetes as well as waist circumference index, height, weight, blood pressure on stock research.
1.2.3. Variables studied:
Age; Gender; Family history related to diabetes; Body mass index (BMI); Measure weight; Waist circumference risk; Hypertension; Examination of venous plasma glucose fasting; Lipid tests; Microalbuminuria:
All data collected through questionnaires given to the computer for processing by the method of biostatistics. Using SPSS 21.0 software. There was statistically significant when p <0.05.
III. RESEARCH RESULTS
2.1. Risk factors feature of research subjects:
Table 2.1. Age group :
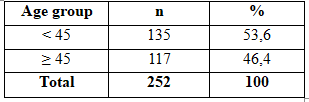 Table 2.2. Gender
Table 2.2. Gender
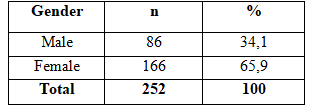 Table 2.3. Family history practices related to diabetes
Table 2.3. Family history practices related to diabetes
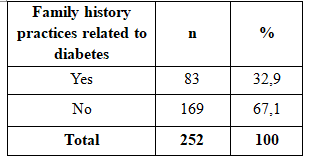 Table 2.4. overweight- obese
Table 2.4. overweight- obese
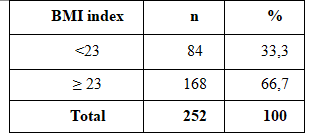 Table 2.5 Risk waist circumference ratio
Table 2.5 Risk waist circumference ratio
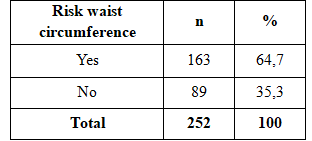 Table 2.6. Dyslipidemia
Table 2.6. Dyslipidemia
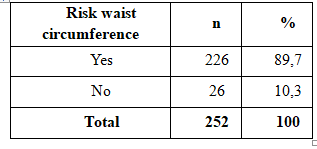
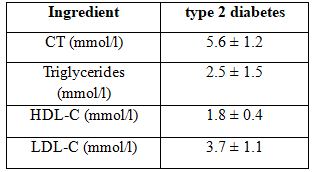
Table 2.7. Blood lipid profile characteristics
 2.2. The rate of hypertension in research subjects :
2.2. The rate of hypertension in research subjects :
Table 2.1. The rate of hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes discovered for the first time
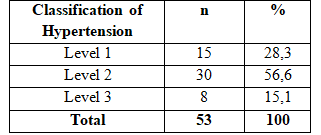
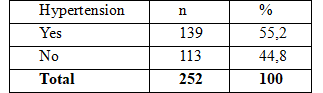 Table 2.2. Level hypertension
Table 2.2. Level hypertension
 2.3. Relationship between hypertension with some risk factors :
2.3. Relationship between hypertension with some risk factors :
2.3.1. The relationship between hypertension and some risk factors
Table 2.3. Association between hypertension with age
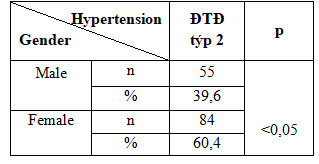 Table 2.4. Association between hypertension with gender:
Table 2.4. Association between hypertension with gender:
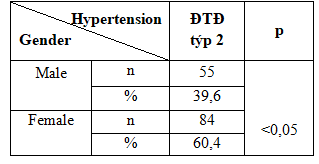
Table 2.5. Association between hypertension and family history are related to diabetes.
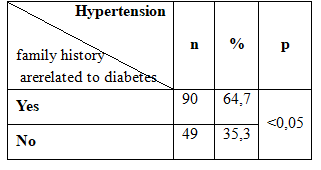 Table 2.6 . Association between hypertension with BMI.
Table 2.6 . Association between hypertension with BMI.
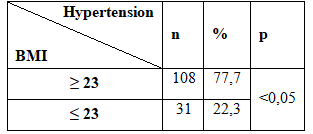 Table 2.7. Association between hypertension with waist circumference risk:
Table 2.7. Association between hypertension with waist circumference risk:
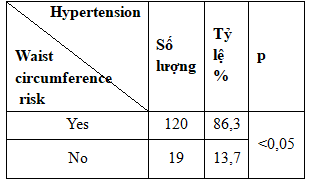 Table 2.8. Association between hypertension and microalbuminuria
Table 2.8. Association between hypertension and microalbuminuria
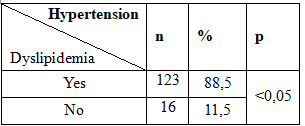
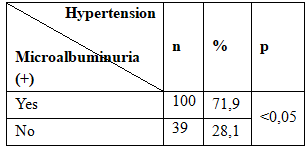 Table 2.9. Association between hypertension and dyslipidemia
Table 2.9. Association between hypertension and dyslipidemia
III. DISCUSS
3.1. The proportion of study subjects with hypertension:
The result of the study we found that the proportion Hypertension in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus is first detected 55.2%. In Vietnam, the percentage of diabetic patients with hypertension 50-70%. Therefore in these patients, in addition to controlling blood glucose and hypertension regardless of other risk factors for heart disease . The degree of hypertension level 2 in patients with type 2 diabetes discovered for the first time accounted for the highest rate, followed by level 1 and level 3 hypertension.
3.2. The relationship between hypertension and some risk factors :
3.2.1. Association between hypertension and age:
According rate results on our research, the rate of hypertension in the group ≥ 45 years of age of subjects with type 2 diabetes accounting for 71.2% higher compared to subjects <45 years of age at the rate of 28.8%. This difference was statistically significant (p <0.05). In our research shows that the higher the rate of hypertension age increasing. This result is consistent with the findings of Nguyen Thi Thu Trang, Authors Nguyen Khoa Dieu Van showed that the rate of hypertension in 50-59 age group is 55.2%, those aged over 70 is 84.5%. This is consistent with the pathophysiology of hypertension.
3.2.2. Association between hypertension with gender:
Male percentage of 34.1%, women 65.9% occupancy rate. In men, the rate is 39.6% lower compared with 60.4% for females. The difference was statistically significant (p <0.05). The results of our research in line with findings of author Nguyen Thi Thien Trang and Tran Thi Ngoc Thu (2012) when the recorded rate of hypertension in women with type 2 diabetes accounting for 78.9 percentage % higher than men accounted for 21.1%
3.2.3. Association between hypertension and family history related to diabetes:
Family history related to diabetes include people who have almost immediate parent, sibling were mellitus duong.Trong our study, the subjects had a family history of related to diabetes in type 2 diabetes accounting for 32.9%. The rate of hypertension in those with a family history of diabetes is related to type 2 diabetes in subjects accounted for 64.7% higher than the group with no history of diabetes related to a ratio of 35.3%. The difference was statistically significant with p <0.05.
3.2.4. Association between hypertension and waist circumference risk:
Audience research-risk waistline is 64.7% occupancy rate. The rate of hypertension in subjects with waist circumference accounted for 86.3% risk was higher in the group with normal waist circumference ratio of 13.7%. The difference was statistically significant (p <0.05). Findings crabs we fit the author’s research in the country is The rate of hypertension among patients with high-risk waist circumference than those no-risk waist circumference.
3.2.5. Hypertension associated with microalbuminuria:
The results of our research on the positive rate of microalbuminuria in subjects with diabetes have lower blood pressure than the findings of Nguyen Thi Thu Thao Nguyen Thy Khue noted billion charter positive microalbuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes accounting for 72.9% of hypertension and the author Tran Thi Ngoc Thu when studying the association between microalbuminuria with certain risk factors interventions in patients with type 2 diabetes, recorded a positive rate of microalbuminuria in patients with diabetes have hypertension was 41.5%.
3.2.7. Association between hypertension and dyslipidemia:
Group objects with type 2 diabetes have dyslipidemia proportion of 89.7% among the principal findings of our study reported the incidence of hypertension in those with dyslipidemia proportion 88.5% higher than in subjects without dyslipidemia proportion is only 11.5%. The results of our research in line with findings by Nguyen Thanh Huyen and his colleagues recorded the growth rate and increased cholesterol triglycerid in Patients with hypertension and among patients with hypertension have no differences with statistical significance (62.5% versus 43.7%; 34.7% versus 15.6%, p <0.05).
IV. CONCLUDE
By studying the characteristics of hypertension in 252 subjects with type 2 diabetes discovered for the first time we recorded the following results:. The rate of hypertension in patients with type 2 diabetes discovered for the first time was 55.2% especially in the second level hypertension which accounts for the highest rate, followed by level 1 and level 3 hypertension.. The rate of hypertension: in subjects ≥ 45 years of age is 71.2% higher than in subjects <45 years of age accounted for 28.8% (p <0.05). Increasing age, the level of hypertension is increasing ; In subjects with a family history of the disease related to diabetes is 64.7% higher than in subjects without a family history of diabetes-related diseases account for only 35.3% (p <0.05).; In subjects with BMI ≥ 23 (overweight, obesity) was 77.7% higher than in subjects with a BMI <23 was 22.3% (p <0.05).; In subjects waist circumference was 86.3% risk compared with subjects without risk waist circumference was 13.7% (p <0.05) ; In subjects with positive microalbuminuria is 71.9% higher than in subjects without microalbuminuria (+) was 28.1% (p <0.05).; In dyslipidemia group proportion 88.5% higher than those without dyslipidemia accounted for only 11.5% (p <0.05).
REFERENCES
- Ta Van Binh (2006), “Kidney disease of diabetes,” Diabetes blood glucose -Increase, -2006 Medical Publishers, pp 473- 524.
- Doan Thi Kim Chau (2010), microscopic study of microalbuminuria in patients with metabolic syndrome at the Central Hospital in Can Tho, specialist secondary thesis, Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy, p 60 -73.
- Tran Hữu Dàng (2008), “Diabetes”, Lecture postgraduate specialized endocrine and metabolic, Hue University Publishers, pp 221-244.
- Nguyen Kim Luong (2010), “Study of some common chronic complications in patients with type 2 diabetes at the Central Hospital of Taiyuan”, Proceedings of the full text of scientific research -Meeting diabetes, endocrine and metabolic disorders central Seventh, practice medical Journal, pp 240-246.
- Vu Bich Nga, Trinh Kim Giang (2010), ” some commented on the situation of complications in patients with glomerulonephritis type 2 diabetes treated at the department of Endocrinology at Bach Mai Hospital “, Journal of endocrinology diabetes, pg 40-45.
- Nguyen Thi My Thao (2012), Research Bilan lipids in patients with pre-diabetes, Doctor Thesis, Hue Medical and Pharmaceutical University, pp 42-43.
- Nguyen Hai Thuy, Le Van Chi (2013), “Diabetes,” Documentation updates diabetes, pp 1-11.
- Nguyen Hai Thuy, Le Van Chi (2013), “Can Classify diabetes,” Diabetes Update, pp 12-20.
- Tran Thi Ngoc Thu (2012), Research microalbuminuria and some risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes, specialist secondary thesis, Hue Medical and Pharmaceutical University, pp 80-82.
- Afghahi H, Cederholm J, Elisasson B (2011), Risk factors for thedeveloppment of albuminurea and renal impairment in type 2 diabetes,Nephrol Dial Transplant, 26, pp.1236 – 1243.
- Ahmadani Muhammad Yakoob, Basit Abdul, Hydrie Zafar Iqbal (2008),Microalbuminurea prevalence study in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes in Pakistan,J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad, 20(3), pp.117-120.
- American Diabetes Association (2011), Standards of medical care in diabetes,Diabetes Care, 34, pp.S11- S61.
- Bosma RJ, Krikken JA, Homan van der Heide (2006), Obesity and renalhemodynamics,Contrib Nephrol, 151, pp.184 – 202.
- Dwyer JP, Parving HH, Hunsicker LG (2012), Renal dysfunction in the presence of normoalbuminurea in type 2 diabetes: Results from the DEMAND Study, Cardiorenal Med, 2, pp.1-10.
- Ejerblad Elisabeth, Fored C, Michael et al (2006), Obesity and risk for chromic renal failure,J Am Soc Nephrol, 17, pp.1695 – 1702.
- Gross Jorge L, Azevedo Mirela J. Silveiro Sandra P, et al (2005),.Diabeticnephropathy: Diagosis, prevention and treatement,Diabetes Care, 28(1), pp 164-176.
- Kambham N, Markowitz GS, Valeri AM (2001), Obesity -related glomerulopathy: an emerging epidemic,Kidney Int, 59, pp.1498 – 1509.
- Kim YI et al (2001), Microalbuminurea is associated with the insulin resistance syndrome independent of hypertension and type 2 diabetes in the Korean population,Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 52(2), pp. 145 – 152.
- Lee Ki Up, Kim Ghi S et al (1995), Prevalence and associated Features of albuminurea in Koreans with NIDDM, Diabetes Care, 18(6), pp.793-799.
- Lin C-C, Liu C-S et al (2007), Microalbuminurea and the metabolic syndrome and its components in the Chinese populaton ,European Journal ofClinical Investigation, 37, pp. 783-790.
- Mogensen CE (1999),Microalbuminurea, blood pressure and diabetes renal disease: orgin and development of ideas,Diabetologia, 42, pp.263-285.
- Niskanen Leo K, Parviainen Markku et al (1996), Evolution, risk factors, and prognostic implications of albuminurea in NIDDM, Diabetes Care, 19(5), pp.486 – 492.
- Palaniappan L et al (2003),Association between microalbuminurea
and the metabolic syndrome: NHANES III,Am J.Hypertension, 16,
pp. 954-957. - Parving H-H, Lewis JB, RavidM, Remuzzi G andHunsicker LG(2006), Prevalence and risk factors for microalbuminuria in a referred cohort of type 2 diabetic patients: A global perspective ,Kidney International, 69, pp. 2057 – 2063.
 Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam
Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam