HYPERTHYROIDISM DURING PREGNANCY
Nguyen The Thanh M.D, Ph.D.
An Sinh Hospital
(Former Head of Endocrinology – Nephropathy Department
Nhan Dan Gia Dinh Hospital)
ABSTRACT
Four pregnant women who were diagnosed gestational transient thyrotoxicosis from 12/2016 to 11/2017 have been followed up until 3/2018. We have some conclusions:
1/ Gestational transient thyrotoxicosis often happens on the first trimester of pregnancy, one patient is on her 8 th week.
2/ Diagnosis based on TSH<0.1mIU/L and high FT4 with beta HCG >50000UI/L, without previous hyperthyrodism history, AntiTPO and TRAb are negative.
3/ Patients don’t need to treat with antithyroid synthesis drugs, they only need to follow up and the thyrotoxicosis will improve in second trimester of pregnancy.
4/ When the stastus of thyrotoxicosis is stable, we need to continue follow up to supplement iode because FT4 may be low especially in twin pregnancy or triple pregnancy.
Main correspondence: Nguyen The Thanh
Submission date: 1st August 2018
Revised date: 18th August 2018
Acceptance date: 31th August 2018
1.INTRODUCTION
In clinical practise, when a patient has hyperthyroidism syndrom we need to confirm this patient suffers from Basedow, toxic adenoma, hypophyse tumor we can begin with antithyroid synthesis drugs or only symptomatic treatment if they suffer from thyroiditis. For pregnant women, we have to confirm whether these women suffer from causes above or they only suffer from gestational transient thyrotoxicosis that only be followed up or treat with small doses of antithyroid synthesis drugs.
If pregnant women have to be accuractely diagnosed the etiology of hyperthyroidism which is treated suitably, both mother and fetus are not harmed.
In this lecture, I limit to gestational transient thyrotoxicosis andpresent some cases of that to find out when they happen during pregnancy, why they were diagnosed, how is treatment, when they are stable, what we should do when the thyrotoxicosis is stable.
2. PATIENTS AND METHODS
A. Patients.
Pregnant women who had manifestations of thyrotoxicosis went to An Sinh outpatient department to be examined in 2016 to 2017.
1. Include criteria.
– Patients with TSH <0,1 mIU/L and high FT4 .
– Without previous history of hyperthyroidism.
– Beta HCG >50.000 IU/L.
2. Exclude criteria
– Without include criteria.
B. Method:
Some cases prospective descriptive study.
3. RESULTS
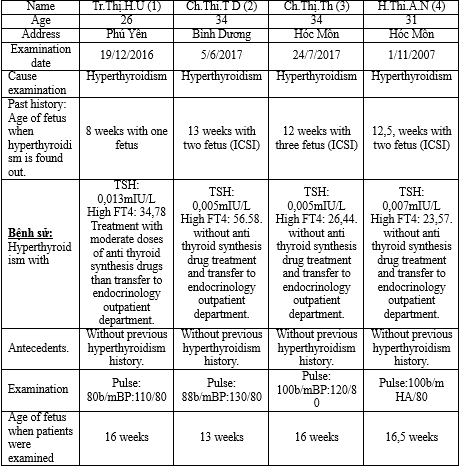
From December /2016 to November /2017 we have four hyperthyroidism pregnant women who have include criteria.
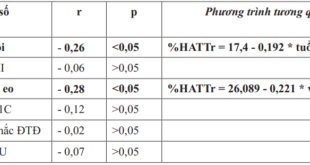
(1): Patient 1; (2): Patient 2; (3): Patient3; (4): Patient4.
ICSI (Intra-Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection)
3. DISCUSSIONS
3.1. Age and the number of fetus
One 26-year old pregnant woman has pregnancy for the first time, 3 other pregnant women who are fertile, need to have ICSI: One 31-year oldpatient (twin pregnancy) and 02 34-year oldpatient (one patient with twin pregnancy, one patient with triple pregnancy).
Besides one patient with one pregnancy, Other three patients, with ICSI, they have from 2 to three fetus so they have more rate of hyperthyroidism: May be because they have more placenta so they have more HCG which have construction like TSH therefore these HCG stimulate the thyroid and make it work more and cause hyperthyroidism. This is suitable with medical documents.
3.2. Fetus ages
These patients were found with hyperthyroidism when they are from 8 weeks to 13 weeks of fetus:
One is on her 8th week, one on her 12th week, one on her 12,5th week and one on her13th week: these facts are reasonable because gestational transient thyrotoxicosis often happens on the first trmester of pregnancy, the highest time of the pick of HCG from 10 to 15 weeks of pregnancy.
Those patients went to out patient department of An Sinh Hospital when the fetus are on 13th to on 16.5th weeks.
01 patient is on her 13th week: Twin pregnancy with TSH:0.005 FT4: 56,58 Beta HCG:329.379.
Twin pregnancy is on the high pick HCG secretion therefore low TSH and clear high FT4 are very reasonable.
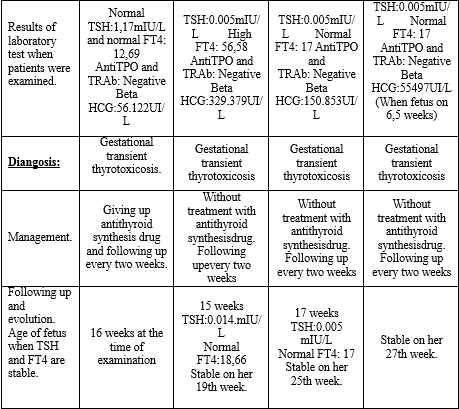
03 other patients are over 16 weeks, at that time their HCG have tendency to decrease so FT4 of two patients return to normal, TSH are still low. 01 patient who was treated with antithyroid drugs, had normal TSH and normal FT4. She has giving up antithyroidsynthesis drugs after ruling out autoimmune hyperthroidism.
3.3. Diagnosis
Both four pregnant women on the first trimester of pregnancy have TSH<0.1mIU/L and high FT4, beta HCG>50000UI/L. Without previous hyperthyroidism history and both of them have Anti TPO and TRAb negative, therefore they are suitable for gestational transient thyrotoxicosis.
3.4. Treatment
Besides one patient who was treated with antithyroid synthesis before going to endocrinology out patient department gave up antithyroid synthesis drug after confirming gestational transient thyroidtoxicosis, three other cases are only followed up. These three patients are stable and don’t need antithyroidsynthesis drugs.
3.5. Following up process
Patient (1) was stable on the first examination, on her 16th week of pregnancy with normal TSH and normal FT4.
This patient is stable until delivery day, she has a baby who in good health up to now.
Patient (2) is stable on her 19th week of pregnancy, patient (3) on her 25th week of pregnancy, patient (4) recovery on 27 weeks of her pregnancy with normal TSH and FT4.
These things show that according medical documents HCG concentration decrease gradually after the first trimester of pregnancy therefore hyperthyroidism also decease later.
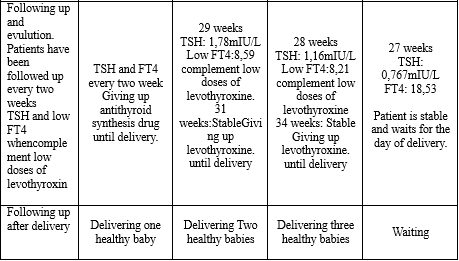
On their 28th and 29th week of pregnancy two patients (2) and (3) have FT4 under normal range, they are treated with low dose of levothyroxin, then iode. These patients are stable until delivery.
One patient has two babies, another patient has three babies, most of them are healthy. This shows that contrary to autoimmune hyperthyrodism when hyperthyroidism is stable we often advise patient to avoid iode salt and iode preparations to prevent hyperthyriodism recurrence.
In these cases when hyperthyroidism is over, FT4 of these patients have tendency to decrease because the iode need of fetus increases especially twin pregnancy or triple pregnancy, therefore, iode complement for these patients when their thyrotoxicosis isover, is reasonable.
Patient (4) is stable and waitsfor delivery.
4. CONCLUSIONS
4 pregnant women who were diagnosed gestational transient thyrotoxicosis from 12/2016 to 11/2017 have been followed up until 3/2018. We have some conclusions:
1/ Gestational transient thyrotoxicosis often happens on the first trimester of pregnancy, one patient is on her 8th week.
2/ Diagnosis based on TSH<0.1mIU/L and high FT4 with beta HCG >50000UI/L, without previous hyperthyroidism history, AntiTPO and TRAb are negative.
3/ Patients don’t need to treat with antithyroid synthesis drugs, but only need to follow up and the thyrotoxicosis will improve in second trimester of pregnancy.
4/ When the ststus of thyrotoxicosis is stable, we need to continue follow up to complement iode because FT4 may be low especially in twin or triple pregnancy.
REFERENCES
- Vũ Bích Nga (Trưởng tiểu ban), Thái Hồng Quang (Chủ biên). Tuyến giáp và thai kỳ. Khuyến cáo về bệnh Nội tiết và Chuyển hóa. tr 63-74. Hội Nội tiết và Đái tháo đường Việt Nam. Nhà xuất bản Y học 2016.
- Glinoer D. The regulation of thyroid function in pregnancy: pathways of endocrine adaptation from physiology to pathology. Endocr Rev. 1997;18:404-33.
- Glinoer D. Thyroid disease during pregnancy. In: Braverman L, Utiger R, eds. The thyroid. 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2000. p. 113-27.
- Glinoer D, deNayer P, Bourdoux P, et al. Regulation of maternal thyroid during pregnanc J Clin Endocrinol Metab.1990;71:276-87.
- Rodien P, Jordan N, Levefre A, et al. Abnormal stimulation of the thyrotrophine receptor during gestation. Hum Reprod Update. 2004;10:95-105.
- M.Albaar, MF.John Adam. Gestational Transient Thyrotoxicosis. Article in Acta medica Indonesiana 41(2):99-104· May 2009 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/24355609_Gestational_transient_thyrotoxicosis
- Yeo C, Khoo D, Eng P, et al. Prevalence of gestational thyrotoxicosis in Asian women evaluated in the 8th to 14th weeks of pregnancy: correlation with total and free beta human chorionic gonadotrophin. Clin Endocrinol (oxf). 2001;55:391-8.
 Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam
Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam