RESEARCH ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN LEPTIN AND INSULIN RESISTANCE IN PREDIABETIC PATIENTS
Tran Minh Triet (1), Nguyen Hai Thuy (2)
(1) University Medical Center at Ho Chi Minh City
(2) Hue University of Medicine and Pharmacy
ABSTRACT
Aims: To evaluate the association between leptin and insulin, insulin resistance in prediabetic population. Patients and Methods: A total 275 prediabetic subjects were included in this study. Collected data were anthropometric characteristics and blood pressure. Fasting blood samples were obtained in early morning and assayed for serum leptin, blood glucose, HbA1c, insulin, lipid profile. Results: The concentration of serum leptin and insulin were 4,58 (2,35-9,00) ng/mL and 8,43 (5,43-12,06)µU/mL, respectively. The prevalence of insulin resistance was 61,5%. In multivariable analysis, insulin resistance was significant associated with age, systolic blood pressure, waist circumference, cholesterol and leptin level. Leptin has a strong association with insulin resistance. Notably, this association is independent of age, gender, BMI, waist circumference and lipid profile. Conclusions: Leptin is positively correlated with insulin resistance and can predict insulin resistance in prediabetic patients.
Keywords: serum leptin, pre-diabetes, insulin resistance, HOMA-IR
Main correspondence: Tran Minh Triet
Submission date: 1st August 2018
Revised date: 18th August 2018
Acceptance date: 31th August 2018
1.INTRODUCTION
The number of patients with type 2 diabetes has been rapidly increasing in both developed and developing countries and its complications account for the majority of the global burden. Today, many studies focus on the early identification and intervention of diabetes, especially at the stage of pre-diabetes. Insulin resistance has an important role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes and especially in prediabetes. Leptin is mainly secreted by adipose tissue and plays an important role in regulating energy homeostasis, food intake and energy expenditure. Both leptin deficiency and leptin resistance can affect glucose metabolism and increase the risk of diabetes. Recent studies showed that leptin level was increased in diabetic patients; therefore leptin could be used to predict future diabetes[11],[15]. However, not all studies reported the increased leptin levels in type 2 diabetes. Some studies on Asian populations pointed out leptin levels tends to be low in diabetes[1],[2]. However, in most studies, the concentration of serum leptin was strongly and positively correlated with insulin resistance regardless of BMI and total body fat mass.
Currently in Vietnam there are few studies that focus on the relationship between leptin and insulin resistance. Thus we wish to perform this study, hoping to strengthen our understanding.
Objectives of this study is to evaluate the association between leptin and insulin, insulin resistance in prediabetes population.
2. PATIENTS AND METHODS
Cross-sectional analysis. Patients were diagnosed pre-diabetes according to the criteria of ADA in 2010 (fasting blood sugar: 100-125 mg/dL or HbA1c: 5.7 – 6.4%) [4]. Control group: healthy individuals with normal blood sugar.
Convenience sampling
Fasting venous blood samples were collected in the morning and measured: glucose (mg%), insulin (microU/ml), total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL – c, HDL-c. HOMA – IR was calculated by [Glucose (mmol/L) x Insulin (mUI/L)]/22,5 and QUICKI was calculated by 1/[log(I0) + log(G0)].
Insulin resistance was defined as the highest quartile of HOMA – IR in control group (≥1.8 in this study). Serum leptin was measured by ELISA method.
Data were analyzed by STATA 12.0.
3. RESULTS
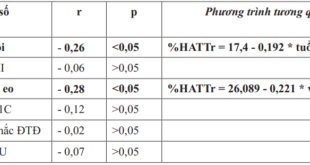
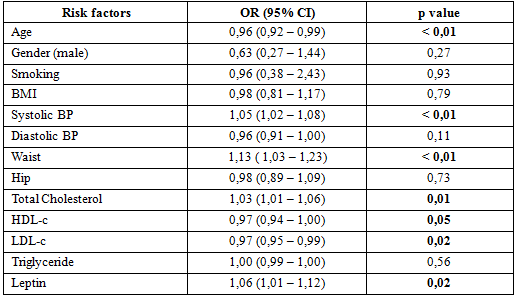
275 pre-diabetic patients participated in this study. The median concentration of leptin and insulin in the study group was 4,58 (2,35-9,00) ng/mL and 8,43 (5,43-12,06)µU/mL respectively. The prevalence of insulin resistance was 61,5%. In multivariate analysis model, we found that insulin resistance was significant associated with age, systolic blood pressure, waist circumference, cholesterol and serum leptin.
Table 1. Characteristics of prediabetic patients
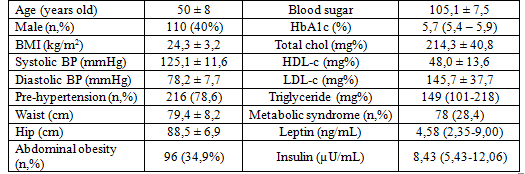
Table 2. Associated factors with insulin resistance in multivariate analysis model
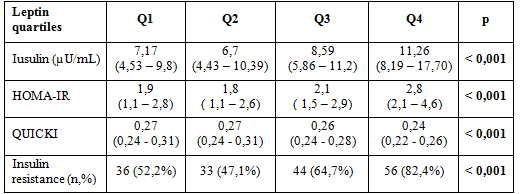
 Leptin has a strong association with insulin resistance regardless of age, gender, BMI, waist circumference and lipid profile in prediabetic patients. Insulin level and insulin resistance were evaluated according to leptin level quartiles. We found that insulin, HOMA-IR and insulin resistance increased with increasing leptin quartiles. Also QUICKI decreased with increasing leptin quartiles. All of differences were significant. Agreeably, insulin level and the rate of insulin resistance were highest at the highest leptin quartile.
Leptin has a strong association with insulin resistance regardless of age, gender, BMI, waist circumference and lipid profile in prediabetic patients. Insulin level and insulin resistance were evaluated according to leptin level quartiles. We found that insulin, HOMA-IR and insulin resistance increased with increasing leptin quartiles. Also QUICKI decreased with increasing leptin quartiles. All of differences were significant. Agreeably, insulin level and the rate of insulin resistance were highest at the highest leptin quartile.
Table 3. Insulin level and insulin resistance according to leptin quartiles
At the level of 4,45 ng/mL, leptin can predict insulin resistance in prediabetic patients with the area under ROC curve was 65% (62% sensitivity and 65% specificity).
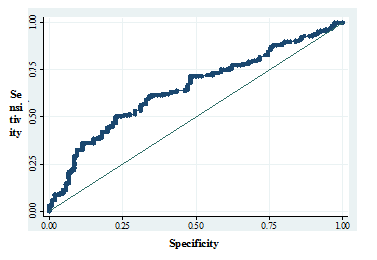
Figure 1. ROC curve for the association between leptin and insulin resistance
4. DISCUSSION
In this study, we found that leptin concentration has a positive correlation with insulin resistance independent of age, gender, BMI, waist circumference and lipid profile in prediabetic patients. Insulin level, HOMA-IR and insulin resistance increased with increasing leptin quartiles and QUICKI decreased with increasing leptin quartiles. Evidently the results were similar to previous studies.
In 2005, a direct correlation between serum leptin and insulin (r=0.598 and p=0.05) in type 2 diabetes was found in a study by Mohiti[8]. In the same year, another experiment performed on a population of Japanese immigrants showed that leptin was significantly correlated to BMI, fat mass, waist circumference, HOMA-IR and serum insulin. The correlation between leptin and HOMA-IR or fasting insulinemia was maintained after adjustments for body adiposity[3]. A study of 387 participants from 18-65 years old performed by Alireza Esteghamati also demonstrated that high leptin level was associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome independent of BMI[6]. Similar results were found in Taniguchi’s study, in which the author concluded that insulin resistance was independently predicted by serum leptin in non-obese Japanese type 2 diabetic patients[12].
Most of previous studies showed that leptin was directly related to insulin sensitivity, and this relationship was independent of total body fat mass. High leptin level was associated with insulin resistance regardless of BMI. In addition, Segal et al found that basal plasma leptin concentrations were significantly lower in lean insulin-sensitive men compared to that in lean insulin-resistant men (1.90±0.4 vs 4.35±1.21ng/ml, p<0.05) despite identical body composition[10]. Serum leptin concentration contributed to insulin resistance in postmenopausal women and also in men as the result of Radka’s study in 2005[7]. Thiyagarajan et al had the same conclusion. He found that leptin levels had significant positive correlations with plasma insulin (r=0.35, p<0.01) and HOMA-IR levels (r=0.31,p<0.05). The correlation between leptin and HOMA-IR levels was more pronounced and significant among the obese T2DM subjects (r=0.82, p=0.01). Hyperleptinemia reflecting leptin resistance plays an important role in the development of IR in obese T2DM patients, making leptin a possible biomarker for the same[13].
The question is whether leptin directly affects insulin resistance, or insulin resistance promotes leptin synthesis, or both are the direct consequence of overweight or obesity. We need more research to further confirm this association. However, insulin resistance is a result of overweight and obesity through many complex mechanisms, in which adipokines may play an important role. Therefore, some researchers believe that leptin has an important role in the mechanism of insulin resistance. Tsu-Nai Wang performed a study in 35 obese adult participants to investigate the impact of weight loss on insulin resistance and the association between insulin resistance and changes in leptin levels. The obese participants had a mean weight loss of 5.6±3.8 kg followed by a 16.7% and 23.3% reduction in HOMA-IR and leptin (p<0.001) levels. After a multivariable logistic regression analysis, the author found that only leptin was statistically correlated with insulin resistance improvement. This implied that leptin may play a role in the modulation of insulin resistance following weight loss[14]. In 1997, Gunter Muller showed that leptin not only affected beta cells function but could also alter the actions of insulin on target organs. At the same concentration of leptin and insulin, leptin may play a role in the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obese patients or non-insulin dependent diabetes mellitus[9]. Anna M. D’souza reviewed the glucoregulatory actions of leptin and concluded that leptin exerts a plethora of metabolic effects on various tissues such as suppressing the production of glucagon and corticosterone, increasing glucose uptake and inhibiting hepatic glucose output. A more in-depth understanding on the mechanisms regarding the glucoselowering actions of leptin may reveal new strategies for the treatment metabolic disorders[5].
5. CONCLUSION
Leptin and insulin resistance is found to have a positive correlation in this study; as a result, leptin levels can be used to predict insulin resistance in prediabetic patients.
REFERENCES
- Ahsan Kazmi, K. M. T. (2012). Association of leptin with type 2 diabetes in non-obese subjects. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad, 24(3-4), 186-189.
- Al-Shoumer, K. A., Al-Asousi, A. A., Doi, S. A. & Vasanthy, B. A. (2008). Serum leptin and its relationship with metabolic variables in Arabs with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Ann Saudi Med, 28(5), 367-370.
- Almeida-Pititto, B. D., Gimeno, S. G., Sanudo, A., Ribeiro-Filho, F. F., Ferreira, S. R. & Japanese-Brazilian Diabetes Study, G. (2005). Leptin is associated with insulin resistance in Japanese migrants. Metab Syndr Relat Disord, 3(2), 140-146.
- American Diabetes Association. (2010). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2010. Diabetes Care, 33(Supplement 1), S11-S61.
- D’Souza A, M., Neumann, U. H., Glavas, M. M. & Kieffer, T. J. (2017). The glucoregulatory actions of leptin. Mol Metab, 6(9), 1052-1065.
- Esteghamati, A., Khalilzadeh, O., Anvari, M., Rashidi, A., Mokhtari, M. & Nakhjavani, M. (2009). Association of serum leptin levels with homeostasis model assessment and estimated insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome: The key role of central obesity. Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders, 7(5), 447-452.
- Lichnovská, R., Gwozdziewiczová, S., Chlup, R. (2005). Serum leptin in the development of insulin resistance and other disorders in the metabolic syndrome. Biomedical papers, 149(1), 119-126.
- Mohiti J, A. M., Babaei A. (2005). Relation between leptin and insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Endocrinol Metab, 3, 121-125.
- Muller, G., Ertl, J., Gerl, M. & Preibisch, G. (1997). Leptin impairs metabolic actions of insulin in isolated rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem, 272(16), 10585-10593.
- Segal, K. R., Landt, M. & Klein, S. (1996). Relationship between insulin sensitivity and plasma leptin concentration in lean and obese men. Diabetes, 45(7), 988-991.
- Soderberg, S., Zimmet, P., Tuomilehto, J., Chitson, P., Gareeboo, H., Alberti, K. G., et al. (2007). Leptin predicts the development of diabetes in Mauritian men, but not women: a population-based study. Int J Obes (Lond), 31(7), 1126-1133.
- Taniguchi, A., Fukushima, M., Nakai, Y., Kuroe, A., Yamano, G., Yanagawa, T., et al. (2005). Soluble E-selectin, leptin, triglycerides, and insulin resistance in nonobese Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Metabolism, 54(3), 376-380.
- Thiyagarajan Manjuladevi Moonishaa & Sunil Kumar Nanda (2017). Evaluation of Leptin as a Marker of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. International Journal of Applied and Basic Medical Research, 7, 176-180.
- Wang TN, Chang WT & Chiu YW. (2013). Relationships between changes in leptin and insulin resistance levels in obese individuals following weight loss. Kaohsiung J Med Sci., 29(8), 436-443.
 Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam
Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam Hội Nội Tiết – Đái Tháo Đường Miền Trung Việt Nam